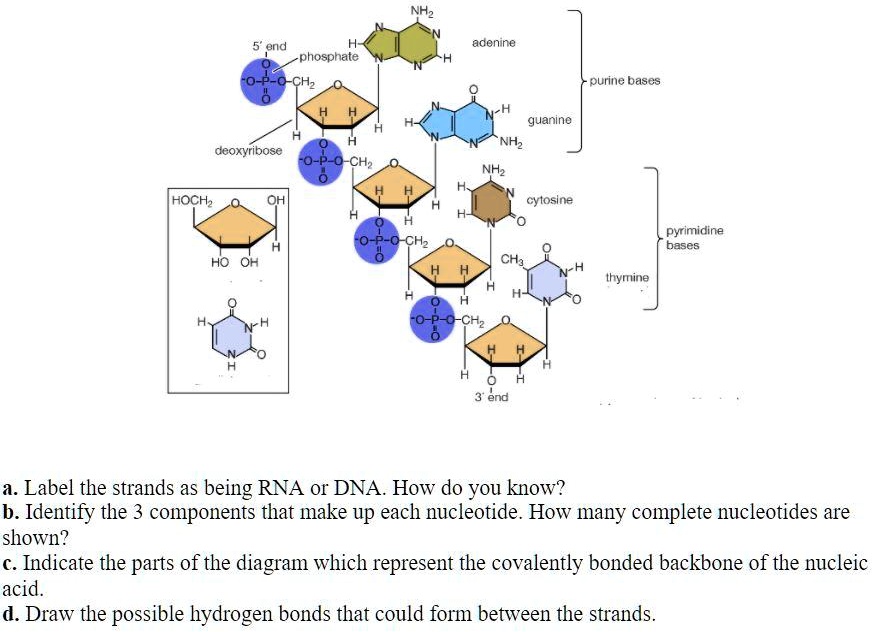
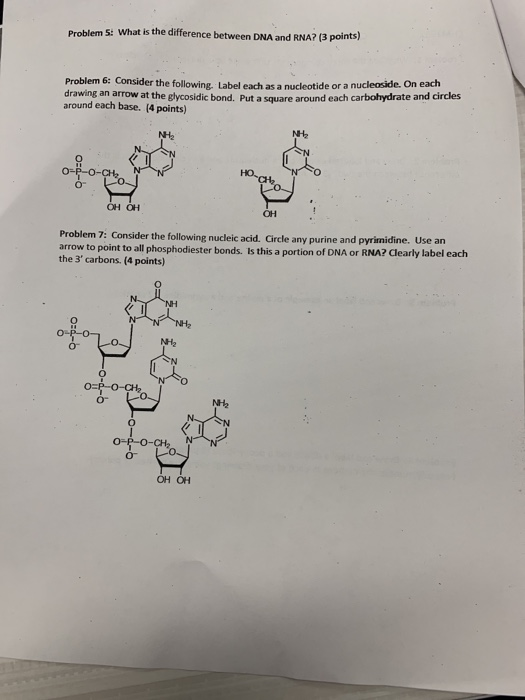
44 draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts
› books › NBK199323 Genetics and Health - NCBI Bookshelf May 15, 2006 · At other levels, cells regulate gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA folding, histone acetylation, and methylation (i.e., chemical modification) of the nucleotide bases. These mechanisms are likely to be influenced by genetic variations in the target genes as well as variations manifested in translated cellular ... › articles › s41576/022/00515-3The emerging landscape of spatial profiling technologies ... Jul 20, 2022 · The sample was imaged to determine the colour assigned to each RNA; FISH probes were removed by digestion; and the sample was re-stained to assign each RNA a second of the four colours.
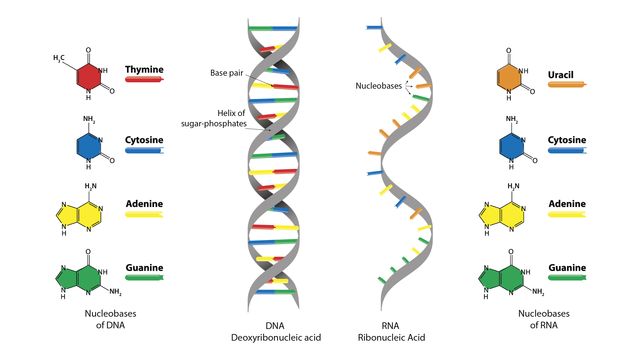
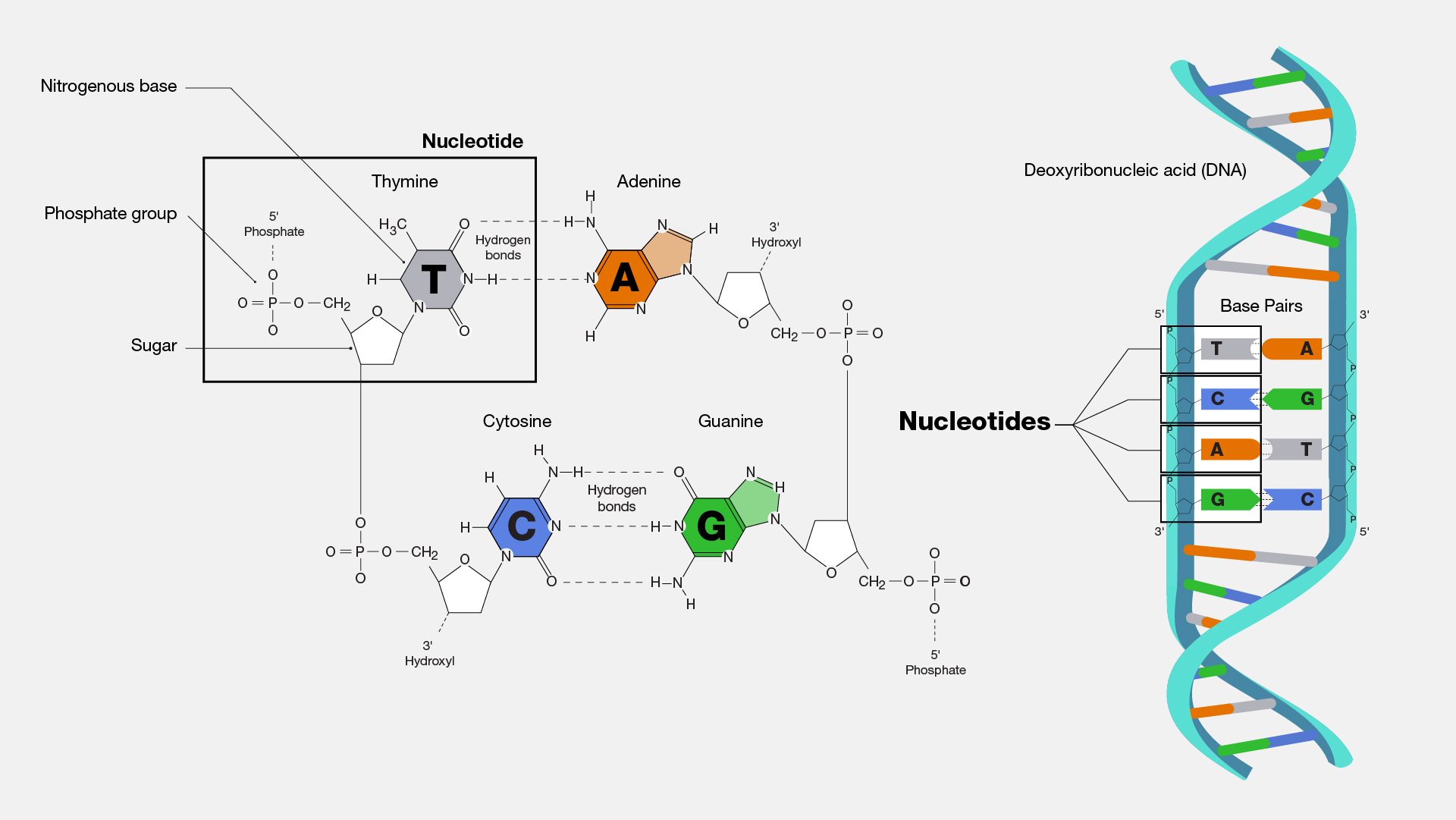
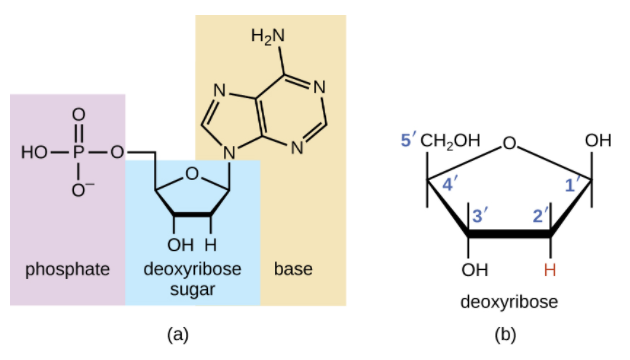
CK12-Foundation A nucleic acid is an organic compound, such as DNA or RNA, that is built of monomers called nucleotides. Many nucleotides bind together to form a chain called a polynucleotide. The nucleic acid DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) consists of two polynucleotide chains. The nucleic acid RNA (ribonucleic acid) consists of just one polynucleotide chain.
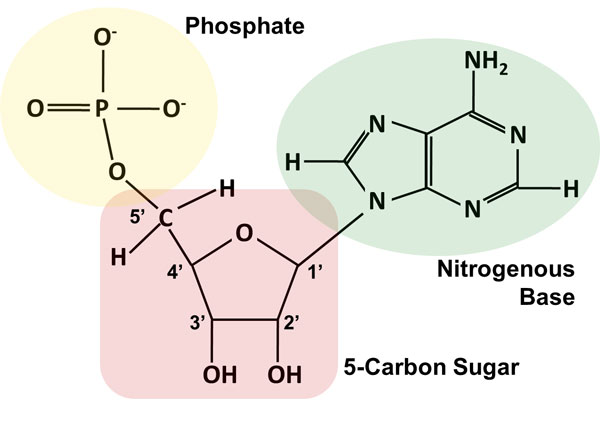
Draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts
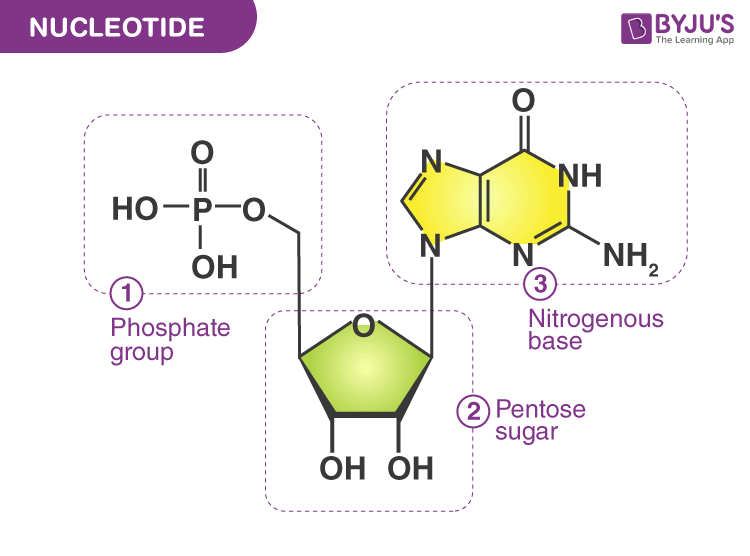
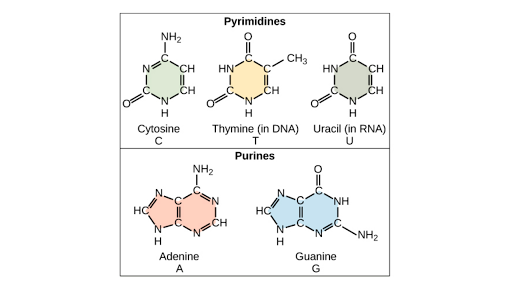
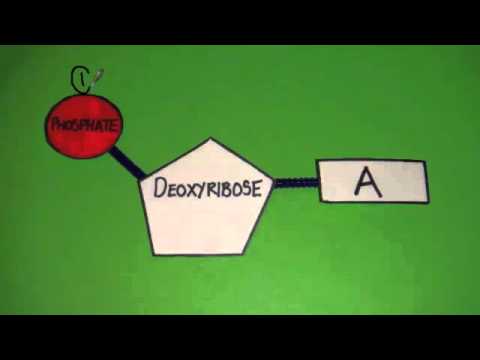
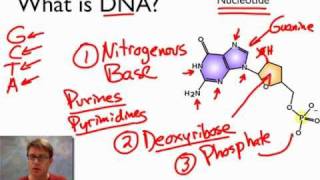
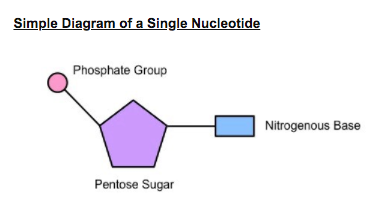
7 Monomers of DNA and RNA | Their Chemistry and Structure - Study Read Ribose sugar molecule. Deoxyribose sugar molecule. Adenine. Guanine. Thymine. Cytosine. Uracil. As the name indicates, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acids) and RNA (ribonucleic acids) have a similar structure and are made of similar monomers. They are made of nuclear bases and carbohydrate monomers. Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). Draw a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts 1. Using the Philippine map (figure 2), plot the location of the following volcanoes. Use the colors indicated in the legend. 4. It is an element that doesn't have the characteristics of metal. 5. It is an element that having the nature of metal. 9. A place that is disorderly ….
Draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts. Discuss the major differences between DNA and RNA and how DNA ... Similarities between tráf replication, transcription & translation thinking questions nucleotide & an rna nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 1. Draw a dna 2. What are the three major differences between d na & rna? A) b) c) 3. What is the... Posted 7 months ago Q: Nucleotides, DNA, and RNA - Knowledge @ AMBOSS nucleotide is comprised of a sugar, a phosphate residue, and a nitrogenous bases (a purine or pyrimidine ). DNA is longer than RNA and contains the entire genetic information of an organism encoded in the sequences of the bases. In contrast, RNA only contains a portion of the information and can have completely different functions in the cell. DNA › books › NBK21136Understanding a Genome Sequence - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf If a northern blot of cellular RNA is probed with a labeled fragment of the genome, then RNAs transcribed from genes within that fragment will be detected . Northern hybridization is therefore, theoretically, a means of determining the number of genes present in a DNA fragment and the size of each coding region. There are two weaknesses with ... Dna Model: Types of DNA, Levels, Structure, Diagram - Embibe DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the largest macromolecule or biopolymer that is made up of small monomeric units called nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. DNA carries the genetic instructions for the functioning, development, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
EOF Label the correct parts of the DNA molecule during transcription. Similarities between tráf replication, transcription & translation thinking questions nucleotide & an rna nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 1. Draw a dna 2. What are the three major differences between d na & rna? A) b) c) 3. What is the... What Is DNA? Summary, Structure, and Importance - Healthline The two strands of DNA form a 3-D structure called a double helix. When illustrated, DNA looks like a spiral ladder in which the base pairs are the rungs, and the sugar-phosphate backbones are the ... Nucleotide Structure, Parts & Function | What is a Nucleotide? - Video ... Nucleotide Structure. A nucleotide's structure consists of: . a 5-carbon sugar; a phosphate group and ; a nitrogenous base.; Each of these elements will now be discussed in detail. The sugar found ...
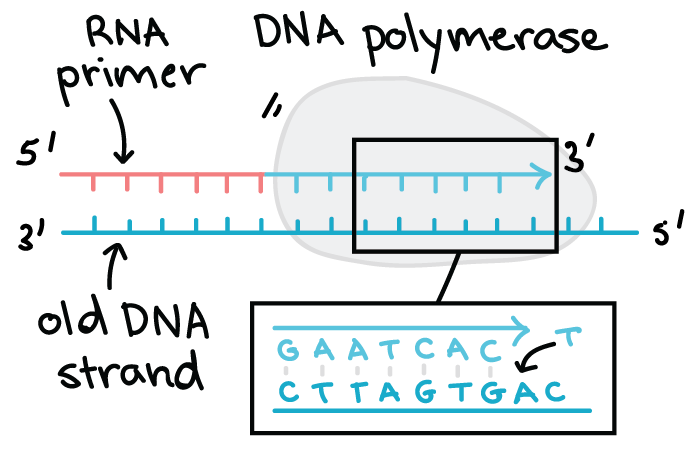
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) - Genome.gov Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and ... › RNA › tutorialViennaRNA Tutorial - Theoretical Biochemistry Group Aug 02, 2017 · The third line shows a condensed representation of the pair probabilities of each nucleotide, similar to the dot-bracket notation, followed by the ensemble free energy (-kT ln(Z)) in kcal/mol. The next two lines represent the centroid structure with its free energy, its distance to the ensemble and the MEA. Crumpled paper and pencil - Brainly.ph Draw a DNA nucleotide & an R nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts 2 What are three major difference between ONA & RNA? 3. What is the p … oint of DNA replic When & where does replication ar? 3 What is the point of transcription en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia This process involves the formation of new protein molecules from amino acid building blocks based on information encoded in DNA/RNA. Protein synthesis generally consists of two major steps: transcription and translation. Transcription is the process where genetic information in DNA is used to produce a complementary RNA strand.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Computational_biologyComputational biology - Wikipedia A nuclear profile is simply this strip or slice that is taken from the nucleus. Each nuclear profile contains genomic windows, which are certain sequences of nucleotides - the base unit of DNA. GAM captures a genome network of complex, multi enhancer chromatin contacts throughout a cell. Neuroscience
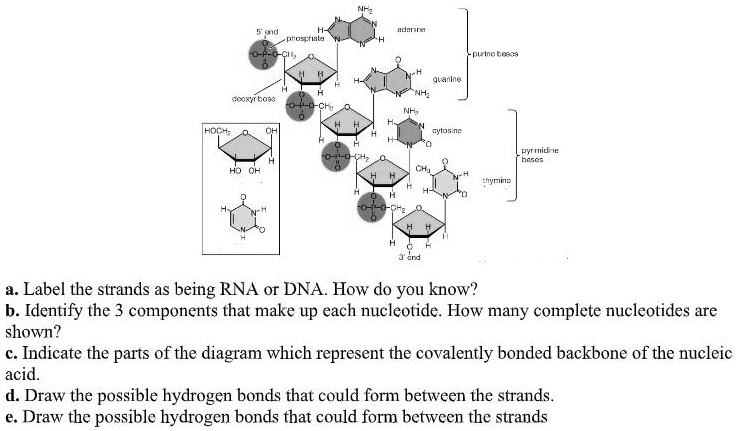
The Differences Between DNA and RNA Explained With Diagrams Pentose sugar in the nucleotide of DNA is deoxyribose whereas in the nucleotide of RNA it is ribose. DNA is copied via self-replication while RNA is copied by using DNA as a blueprint. DNA uses thymine as a nitrogen base while RNA uses uracil. The difference between thymine and uracil is that thymine has an extra methyl group on the fifth carbon.
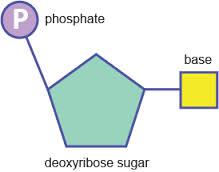
What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io DNA, and other nucleic acids such as RNA, are made up of nucleotides. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The structure ofDNA's can be visualized or thought of like a ladder. If we continue with this analogy, each "step or rung" of this ladder is made up of a string of nucleotides, in a very specific and controlled order.
RNA and Proteins - BrainMass 1. Describe, in general terms, the steps involved in the automated synthesis of the DNA sequence GCT. 2. Draw and label the four DNA nucleosides. 3. Draw and label a G-C base pair. Indicate all hydrogen bonds with a dashed line. 4. Draw and label an A-T base pair. Indicate all hydrogen bonds with a dashed line. 5. Of
What's the Difference Between a DNA and RNA Vaccine? - Verywell Health Another difference between a DNA and RNA vaccine is that a DNA vaccine delivers the message via a small electrical pulse, which "literally pushes the message into the cell," Cifuentes-Kottkamp says. "The advantage is that this vaccine is very stable at higher temperatures. The disadvantage is that it requires a special device that ...
› 2072/6694/14-15 › 3628Cancers | Free Full-Text | Techniques for Profiling the ... Jul 26, 2022 · In recent years there has been increased interest in using the immune contexture of the primary tumors to predict the patient’s prognosis. The tumor microenvironment of patients with cancers consists of different types of lymphocytes, tumor-infiltrating leukocytes, dendritic cells, and others. Different technologies can be used for the evaluation of the tumor microenvironment, all of ...
Draw a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts 1. Using the Philippine map (figure 2), plot the location of the following volcanoes. Use the colors indicated in the legend. 4. It is an element that doesn't have the characteristics of metal. 5. It is an element that having the nature of metal. 9. A place that is disorderly ….
Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
7 Monomers of DNA and RNA | Their Chemistry and Structure - Study Read Ribose sugar molecule. Deoxyribose sugar molecule. Adenine. Guanine. Thymine. Cytosine. Uracil. As the name indicates, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acids) and RNA (ribonucleic acids) have a similar structure and are made of similar monomers. They are made of nuclear bases and carbohydrate monomers.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)
















Post a Comment for "44 draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts"