43 homolougous structures
Homologous Structures: Definition And Examples - Science Trends The term "homologous structures" refers specifically to similar structures found in different species that have a common ancestry or developmental origin. Note that homologous structures don't have to perform the same function in a species, the only requirement is that they are similar in form and exist in species with common ancestry. Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures Homologous structures exhibit similar anatomy, though dissimilarity in functions, in analogous structure there is dissimilarity in anatomy, but the similarity in their functions. Homologous structures develop in a related species or which shares common ancestors, whereas homologous structures develop in unrelated species. ...
Homologous Structures vs Analogous Structures | Key Differences ( Video ... Homologous and Analogous Structures can be confusing, but it doesn't have to be. We'll talk about the differences and similarities right here in less then 2 minutes! Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. We have a new and improved read on this topic.

Homolougous structures
Homologous vs. Analogous Structures (Video) - Mometrix Homologous Structures When comparing homologous structures, we are comparing the anatomy of one part of an organism to another and finding it to be structurally similar but functionally may be different. Homologous Structures Examples Let's compare a couple of tetrapods, specifically a human arm and a cat arm. Examples of Homologous Structures That Reveal Our Shared Ancestry Homologous structures are structurally and functionally similar and derived from a common ancestor; whereas, analogous structures have similar functions but are not descended from a common ancestor. The term homology was coined in the year 1656. It is derived from the Greek words homos, meaning 'same' and logos, meaning 'relation'. Homologous Structures | Brief Introduction & Examples - iBiologia What are homologous structures: They are defined as the organs or the elements of animals skeletal and organisms that suggest their inheritance from a common ancestor by virtue of their similar properties. These structures do not look exactly similar or the same to each other or have the same functions to do.
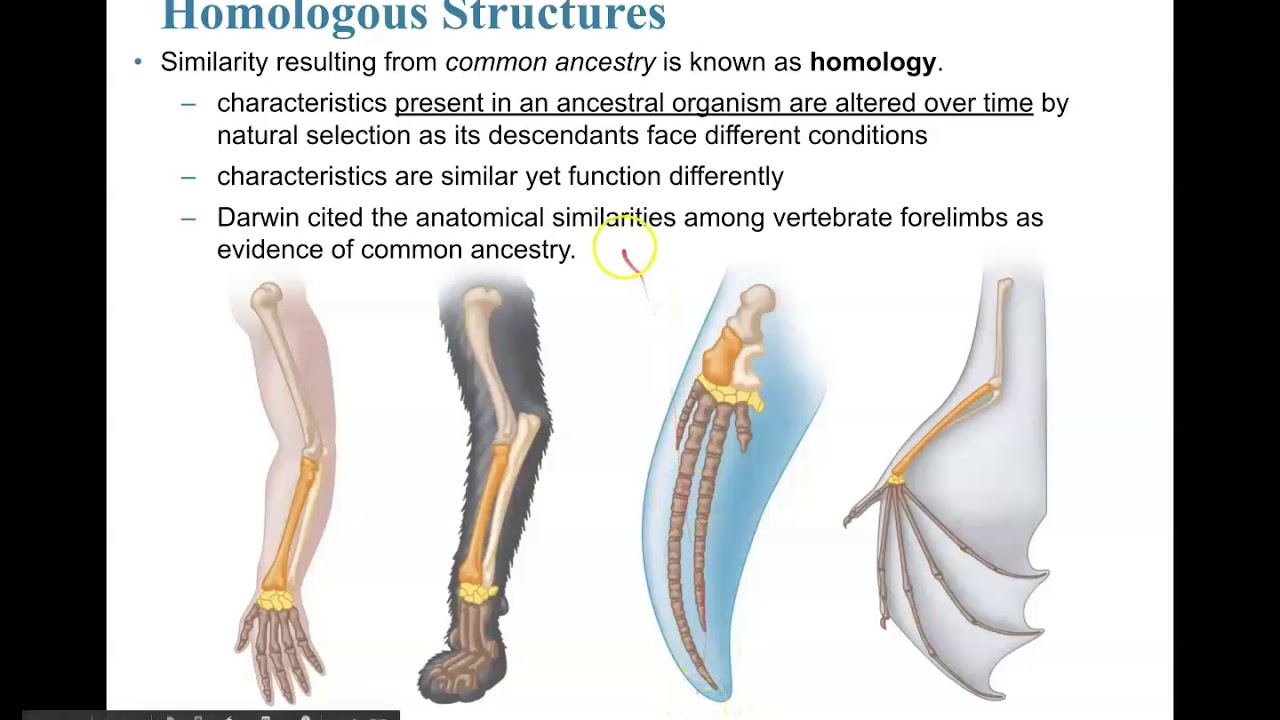
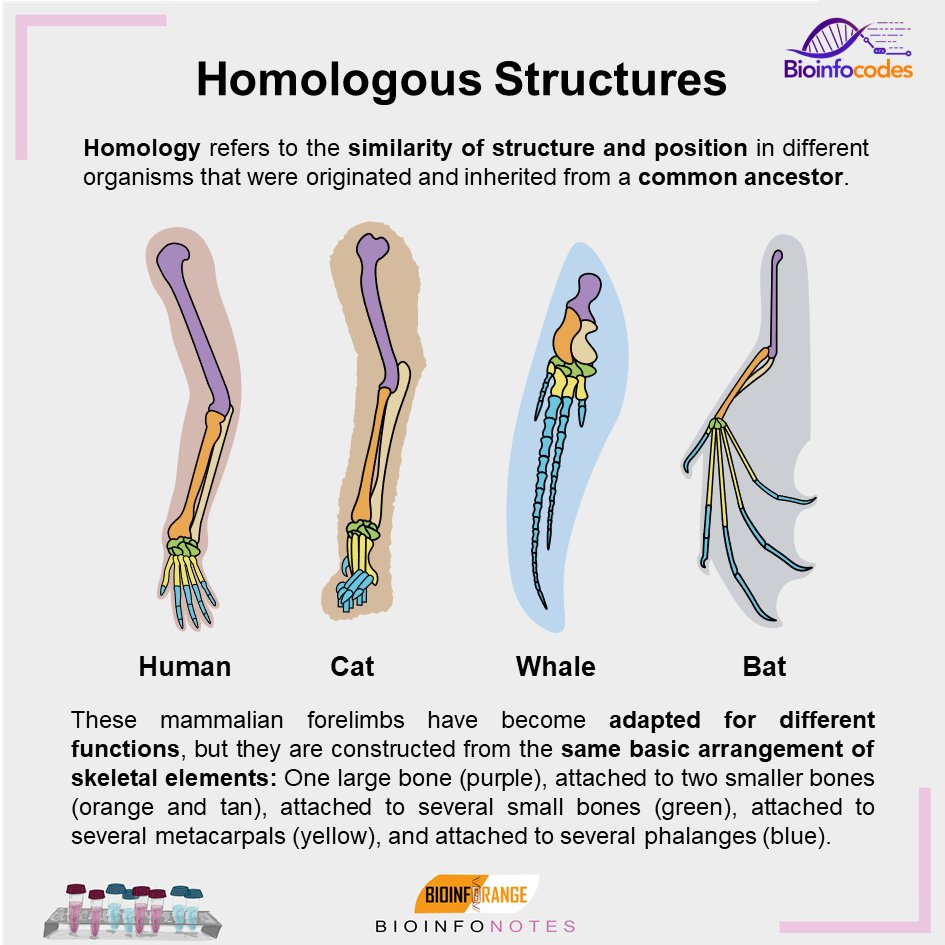
Homolougous structures. Homologous - Definition and Examples | Biology Dictionary "Homologous," in biology, means a similarity in internal or chromosomal structures. With internal structures, homology indicates organs that have similar positions, structures, or evolutionary origins. It's important to note, however, that organs do not have to have the same function to be homologous. Homologous and Analogous Structures: What's the Difference? - PrepScholar Homologous structures are similar structures in related organisms. The most important thing to remember about homologous structures is that they share common ancestry. In other words, only organisms that are somehow related to each other can have homologous structures. For example, a chimpanzee's arm and a human's arm are homologous structures. 8 Top Difference between Homologous and Analogous Structures Homologous structures are anatomical structures that evolved from organisms having the same ancestry. These structures develop from organisms of related species but they do perform different functions. Homologous structures result in divergent evolution. Difference Between Homologous Structures and Vestigial Structures The key difference between homologous structures and vestigial structures is that homologous structures are the anatomically similar structures found in different organisms that share a common ancestor while vestigial structures are the anatomical structures which have lost their usefulness to an organism.. Homologous structures are vestigial structures are two types of anatomical structures ...
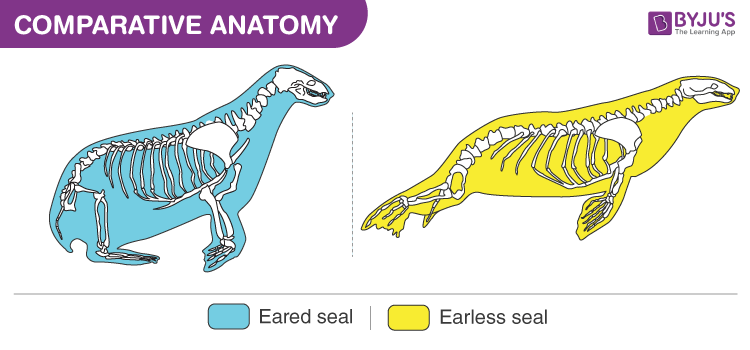
Homologous and analogous structures (with examples) The homologous structure They are parts of a biological organism that share a common ancestor, while analogous ones perform similar functions. When comparing two processes or structures, we can assign them as homologues and analogues. These concepts gained popularity after the emergence of evolutionary theory, and their recognition and ... Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures - VEDANTU Homologous structures can be defined as the organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that, by virtue of their similarity, belong to a common ancestor. These structures do not necessarily have to look exactly the same, or have the same function. For example, the arm of a chimpanzee and the arm of a human are homologous. Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures Homologous structures are those morphological features that are found in organisms that evolved from a common ancestor. This means that closely related species often do share homologous traits which are often of similar structure but may have the same or different function. Degree of relatedness: Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures - BYJUS An arm of a human, the leg of a dog or a flipper of a whale are all homologous structures. From wings in birds, bats and insects to fins in penguins and fishes are all analogous structures. These were a few differences between analogous and homologous structures. From this, we can conclude that the main difference between homologous and ...
10 Difference Between Homologous And Analogous Structures/Organs With ... The traits they share are referred to homologous structures. A homologous structure is an organ or body part that appears in different animals and is similar in structure and location, but doesn't necessarily share the same purpose. This type of evolution is referred to as divergent evolution. What are homologous structures? What are their functions? Answer (1 of 2): Homologous (adj) used in chemistry and biology Having the same relation, relative position, or structure, in particular. BIOLOGY(of organs) similar in position, structure, and evolutionary origin but not necessarily in function."a seal's flipper is homologous with the human arm"... Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures Homologous Structures: Homologous structures can be used to infer evolutionary relationships among species. Analogous Structures: Analogous structures cannot be used to infer evolutionary relationships among species. Conclusion. Homologous and analogous structures are two types of structures found in species as an adaption to the environment ... Homologous Structures Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Biology Roots. 4.9. (178) $3.00. Zip. This is a 3 page activity in which students compare and contrast homologous and analogous structures. This is done via analyzing images, filling in tables and answering questions. There is also a brief section on vestigial structures. 11 questions total. Great for introduction and reinforcement!
What are Homologous Structures in Evolution? - Study.com Homologous structures refer to the same structures that are observed in different species. Homologous structures, while either the same or extremely similar in appearance, may have very different...
Anatomy, Evolution, and Homologous Structures - ThoughtCo As time passed and technology advanced, homologous structures became more important in deciding the final placement on the phylogenetic tree of life . Linnaeus's taxonomy system places species into broad categories. The major categories from general to specific are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
Homologous Structures - Definition and Examples - Biology Dictionary Homologous structures are organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that, by virtue of their similarity, suggest their connection to a common ancestor. These structures do not have to look exactly the same, or have the same function. The most important part, as hinted by their name, is that they are structurally similar.
What is the Difference Between Homologous Structures and Vestigial ... Homologous structures refer to organs or skeletal elements of animals that, by virtue of their similarity, suggest their connection to a common ancestor while vestigial structures refer to the structures in an animal that has lost all or most of its original function in the course of evolution.
homology/homologous structure - Understanding Evolution homology/homologous structure - Understanding Evolution Inherited from a common ancestor. Human eyes and mouse eyes are homologous structures because we each inherited them from our common ancestor that also had the same sort of eyes. Contrast this with homoplasious and analogous. Inherited from a common ancestor.
Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structures What are Homologous Structures? Homologous structures are the organs or the other structures in different animals which descend from a common ancestor. These structures are anatomically similar, but they may perform different functions. Homologous structures are developed in related organisms since they share a common ancestor.
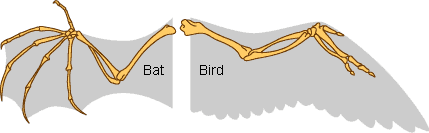
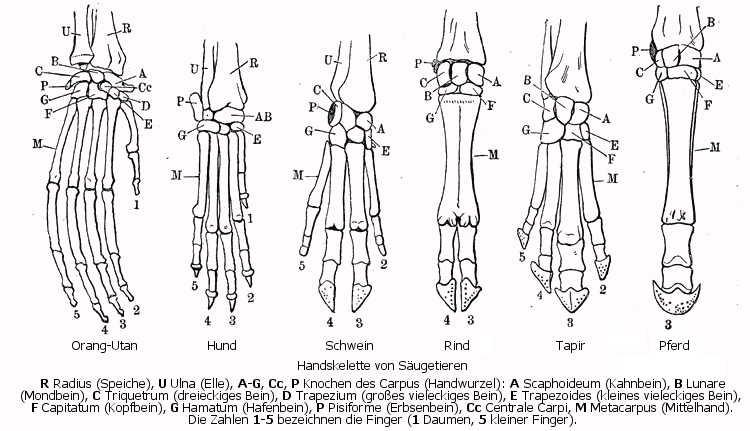
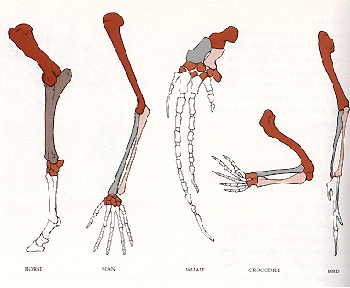
Homologous Structure Examples in Different Organisms - YourDictionary A dolphin's flipper, a bird's wing, a cat's leg, and a human arm are considered homologous structures. Whereas human beings have bones such as the humerus (upper arm), ulna and radius (forearm), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (hand bones), and phalanges (fingers), these features appear as similar bones in form in the other animals.
Homologous Structures: Explanation, Examples, & Traits - Study.com Evolutionary biologists that study genetics of organisms noticed similarities in structures of these organisms even when the function was not the same. These structures are called homologous...
Homologous structures, genes, and developmental pathways Specifically, for anatomical homology, the authors draw the following conclusion: two different animals can be said to have "homologous structures because they were built by homologous genes" through "developmental pathways" that are homologous (p. 41).
Homologous Structures | Brief Introduction & Examples - iBiologia What are homologous structures: They are defined as the organs or the elements of animals skeletal and organisms that suggest their inheritance from a common ancestor by virtue of their similar properties. These structures do not look exactly similar or the same to each other or have the same functions to do.
Examples of Homologous Structures That Reveal Our Shared Ancestry Homologous structures are structurally and functionally similar and derived from a common ancestor; whereas, analogous structures have similar functions but are not descended from a common ancestor. The term homology was coined in the year 1656. It is derived from the Greek words homos, meaning 'same' and logos, meaning 'relation'.
Homologous vs. Analogous Structures (Video) - Mometrix Homologous Structures When comparing homologous structures, we are comparing the anatomy of one part of an organism to another and finding it to be structurally similar but functionally may be different. Homologous Structures Examples Let's compare a couple of tetrapods, specifically a human arm and a cat arm.

















/about-homologous-structures-1224763_sketch_FINAL2-4c326d5ec6a5440d9224580a5bbe36d7.png)










Post a Comment for "43 homolougous structures"